Difference between revisions of "Manual:Timer Engine"
m (→Regular GUI Timers: layout picture) |
(ordering) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{TOC right}} | ||
| + | {{#description2:Manual on handling timers via GUI or Lua code, starting, stopping, nesting, etc.}} | ||
| + | |||
=Timer Engine= | =Timer Engine= | ||
| − | Mudlet supports | + | Mudlet supports four different sorts of timers: |
| + | |||
| + | # [[#Regular GUI Timers|Regular GUI Timers]] | ||
| + | # [[#Temporary Timers|Temporary Timers]] | ||
| + | # [[#Offset Timers|Offset Timers]] | ||
| + | # [[#Stopwatches|Stopwatches]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first can be configured by clicking and will start some code in regular intervals. The others can be used in other scripts you code. All of them are described in more detail below. | ||
==Regular GUI Timers== | ==Regular GUI Timers== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 20: | ||
You can also enable/disable this timer via scripting with [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#enableTimer|enableTimer()]] and [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#disableTimer|disableTimer()]]: | You can also enable/disable this timer via scripting with [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#enableTimer|enableTimer()]] and [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#disableTimer|disableTimer()]]: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
enableTimer("Newbie timer") -- enables the timer, so 2s after being enabled, it'll tick - and every 2s after that | enableTimer("Newbie timer") -- enables the timer, so 2s after being enabled, it'll tick - and every 2s after that | ||
disableTimer("Newbie timer") -- disables it, so it won't go off anymore | disableTimer("Newbie timer") -- disables it, so it won't go off anymore | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
==Temporary Timers== | ==Temporary Timers== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 33: | ||
One thing to keep in mind when working with tempTimers is that they are unlike #wait statements you might see in other clients. While #waits are typically cumulative, tempTimers aren't - they go off from the same point in time. Thus if you'd like two timers to go off - one after 3s, and another 1s after the first one - you'd set the second timer to go off at 4s. For example: | One thing to keep in mind when working with tempTimers is that they are unlike #wait statements you might see in other clients. While #waits are typically cumulative, tempTimers aren't - they go off from the same point in time. Thus if you'd like two timers to go off - one after 3s, and another 1s after the first one - you'd set the second timer to go off at 4s. For example: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
tempTimer(3, [[ echo("this is timer #1 going off 3s after being made\n") ]]) | tempTimer(3, [[ echo("this is timer #1 going off 3s after being made\n") ]]) | ||
tempTimer(4, [[ echo("this is timer #2 going off 4s after being made - and 1s after the first one\n") ]]) | tempTimer(4, [[ echo("this is timer #2 going off 4s after being made - and 1s after the first one\n") ]]) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
{{note}} Temporary timers cannot be accessed from the GUI and are not saved in profiles. | {{note}} Temporary timers cannot be accessed from the GUI and are not saved in profiles. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 43: | ||
To stop a temporary timer once you've made it and before before it went off - you use [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#killTimer|killTimer()]]. You give killTimer(id) the ID of the timer that you've made - which you get from Mudlet when you make it. Here's an example: | To stop a temporary timer once you've made it and before before it went off - you use [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#killTimer|killTimer()]]. You give killTimer(id) the ID of the timer that you've made - which you get from Mudlet when you make it. Here's an example: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
-- get and store the timer ID in the global "greeting_timer_id" variable | -- get and store the timer ID in the global "greeting_timer_id" variable | ||
greeting_timer_id = tempTimer(2, [[ echo("hello!\n") ]]) | greeting_timer_id = tempTimer(2, [[ echo("hello!\n") ]]) | ||
| Line 39: | Line 49: | ||
-- delete the timer - thus nothing will actually happen! | -- delete the timer - thus nothing will actually happen! | ||
killTimer(greeting_timer_id) | killTimer(greeting_timer_id) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
===Refreshing=== | ===Refreshing=== | ||
You can also use [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#killTimer|killTimer()]] to "refresh" a timer - the following code example will delete the previous timer if one exists and create the new one, thus making sure you don't get multiple copies of it: | You can also use [[Manual:Mudlet_Object_Functions#killTimer|killTimer()]] to "refresh" a timer - the following code example will delete the previous timer if one exists and create the new one, thus making sure you don't get multiple copies of it: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
if portal_timer then killTimer(portal_timer) end | if portal_timer then killTimer(portal_timer) end | ||
portal_timer = tempTimer(2, [[ send("enter portal") ]]) | portal_timer = tempTimer(2, [[ send("enter portal") ]]) | ||
| − | </lua> | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| + | |||
| + | === Time remaining === | ||
| + | You can use [[Manual:Mudlet Object Functions#remainingTime|remainingTime()]] to check how much time remains on a provided Timer.<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | tid = tempTimer(600, [[echo("\nYour ten minutes are up.\n")]]) | ||
| + | echo("\nYou have " .. remainingTime(tid) .. " seconds left, use it wisely... \n") | ||
| + | |||
| + | -- Will produce something like: | ||
| + | |||
| + | You have 599.923 seconds left, use it wisely... | ||
| + | |||
| + | -- Then ten minutes time later: | ||
| + | Your ten minutes are up. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===Using variables=== | ===Using variables=== | ||
To embed a value of a variable in tempTimer code, you might try using this given what you've learnt: | To embed a value of a variable in tempTimer code, you might try using this given what you've learnt: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
tempTimer(1.4, [[ echo("hello, "..matches[2].."!\n") ]]) | tempTimer(1.4, [[ echo("hello, "..matches[2].."!\n") ]]) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
But that won't work as you'd expect it to - that will try and use the value of matches[2] ''when the timer goes off'' - while by then, the variable could have changed! Instead, you take it outside the square [[ ]] brackets - this is correct: | But that won't work as you'd expect it to - that will try and use the value of matches[2] ''when the timer goes off'' - while by then, the variable could have changed! Instead, you take it outside the square [[ ]] brackets - this is correct: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
tempTimer(1.4, [[ echo("hello, ]]..matches[2]..[[!\n") ]]) | tempTimer(1.4, [[ echo("hello, ]]..matches[2]..[[!\n") ]]) | ||
| − | </ | + | |
| + | -- or with less brackets: | ||
| + | tempTimer(1.4, function() echo("hello, "..matches[2].."!\n") end) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===Nesting=== | ===Nesting=== | ||
If you'd like, you can also nest tempTimers one inside another - though the first [[]]'s will become [=[ ]=]: | If you'd like, you can also nest tempTimers one inside another - though the first [[]]'s will become [=[ ]=]: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
tempTimer(1, [=[ | tempTimer(1, [=[ | ||
echo("this is timer #1 reporting, 1s after being made!\n") | echo("this is timer #1 reporting, 1s after being made!\n") | ||
| Line 72: | Line 99: | ||
]]) | ]]) | ||
]=]) | ]=]) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
If you'd like to nest more of them, you'd increase the amount of ='s on the outside: | If you'd like to nest more of them, you'd increase the amount of ='s on the outside: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
tempTimer(1, [==[ | tempTimer(1, [==[ | ||
echo("this is timer #1 reporting, 1s after being made!\n") | echo("this is timer #1 reporting, 1s after being made!\n") | ||
| Line 87: | Line 114: | ||
]=]) | ]=]) | ||
]==]) | ]==]) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
===Closures=== | ===Closures=== | ||
| − | Last but not least, you can also use [http://www.lua.org/pil/6.1.html closures] with tempTimer - using a slightly different syntax that has advantages | + | Last but not least, you can also use [http://www.lua.org/pil/6.1.html closures] with tempTimer - using a slightly different syntax that has advantages. For example, you have access variables in its scope, when it goes off: |
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
local name = matches[2] | local name = matches[2] | ||
tempTimer(2.4, function() echo("hello, "..name.."!\n") end) | tempTimer(2.4, function() echo("hello, "..name.."!\n") end) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| + | |||
| + | Also syntax highlighting will work as expected, because the function will not be given as a string. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{note}} In this case, you mustn't use matches[2] directly in the echo() command. It will not work as expected. Instead, bind the it to a new variable like name as seen in the example above. | ||
==Offset Timers== | ==Offset Timers== | ||
| − | <span style="color:#0000FF">'''Offset Timers'''</span> are child timers of a parent timer and fire a single shot after a specified timeout after their parent fired its respective timeout. This interval is an offset to the interval of its parent timer. To make them, add a regular GUI timer (see above), then create another timer and '''drag it onto the timer'''. This will make the timer that is "inside" the timer (the child inside the parent) go off at a certain time after | + | <span style="color:#0000FF">'''Offset Timers'''</span> are child timers of a parent timer and fire a single shot after a specified timeout after their parent fired its respective timeout. This interval is an offset to the interval of its parent timer. To make them, add a regular GUI timer (see above), then create another timer and '''drag it onto the timer'''. This will make the timer that is "inside" the timer (the child inside the parent) go off at a certain time after its parent goes off. Offset timers differ visually from regular timers and are represented with a + icon for offset. Offset timers can be turned on and off by the user just like any other timer. For example - a parent timer fires every 30 seconds and by doing so kicks off 3 offset timers with an offset of 5 seconds each. Consequently, the 3 children fire 5 seconds after each time the parent timer fired. To make this happen, make the parent timer tic every 30 seconds, drag 3 timers into it with an offset of 5s on each: |
[[File:Offset timers.png|center]] | [[File:Offset timers.png|center]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Uses and examples== | ==Uses and examples== | ||
| Line 114: | Line 138: | ||
This'll make use of tempTimer to enable a trigger and disable it after a short period of time: | This'll make use of tempTimer to enable a trigger and disable it after a short period of time: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
enableTrigger("Get enemy list") | enableTrigger("Get enemy list") | ||
tempTimer(3, [[disableTrigger("Get enemy list")]]) | tempTimer(3, [[disableTrigger("Get enemy list")]]) | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
=== Running a script after the current triggers === | === Running a script after the current triggers === | ||
A useful trick to get your code to run right after all of the current triggers (GUI and temporary) ran would be to use a time of 0: | A useful trick to get your code to run right after all of the current triggers (GUI and temporary) ran would be to use a time of 0: | ||
| − | <lua> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
-- in a script, this will run after all scripts were loaded - including the system, wherever in the order it is. | -- in a script, this will run after all scripts were loaded - including the system, wherever in the order it is. | ||
tempTimer(0, function() | tempTimer(0, function() | ||
| − | + | print("this timer is running after all triggers have run") | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
end) | end) | ||
| − | </lua> | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| + | |||
| + | Have more examples you'd like to see? Please add or [https://discord.gg/kuYvMQ9 request them]! | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Stopwatches == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The stopwatch feature can be used to time how long things take, e.g. long running functions or how long a fight lasts. Stopwatches can be started, stopped and reset just like a regular physical stopwatch. They can also be given a name and made to be persistent, meaning that they can keep running (or timing) when Mudlet has been closed. This gives you the ability to time real-life events. Of course, you can also query how much time has passed and delete a stopwatch no longer required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Creating and Starting === | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch() -- create, or re-use a stopwatch, and store the watch variable ID in a global variable to access it from anywhere | ||
| + | |||
| + | -- then you start the stopwatch in some trigger/alias/script with; | ||
| + | startStopWatch(fightStopWatch) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The watch will now be running. Alternatively, you can create and instantly start a stopwatch in one line; | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |
| + | fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch(true) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Manual:Lua_Functions#createStopWatch|createStopWatch()]], [[Manual:Lua_Functions#startStopWatch|startStopWatch()]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Stopping and Resetting === | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can stop a stopwatch and retrieve its run time as follows; | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | -- in a trigger script for example you can write: | ||
| + | fightTime = stopStopWatch(fightStopWatch) | ||
| + | echo("The fight lasted for " .. fightTime .. " seconds.") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then reset it for the next fight. | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | resetStopWatch(fightStopWatch) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that resetting a stopwatch does not stop or start it, it's simply resets the time value to zero. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Manual:Lua_Functions#stopStopWatch|stopStopWatch()]], [[Manual:Lua_Functions#resetStopWatch|resetStopWatch()]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Deleting a Stopwatch === | ||
| + | |||
| + | To delete a stopwatch and free up the variable ID simply; | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | deleteStopWatch(fightTime) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Manual:Lua_Functions#deleteStopWatch|deleteStopWatch()]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === More Ways to Retrieve Running Time === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The time can be retrieved at any point of a started and currently running or stopped stopwatch. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <code>getStopWatchTime</code> - returns the time as a decimal number of seconds with up to three decimal places to give a milli-seconds | ||
| + | * <code>getStopWatches</code> - returns a table of the details for each stopwatch in existence | ||
| + | * <code>getStopWatchBrokenDownTime</code> - returns a table of times for a given stopwatch; days, hours, minutes, etc... | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Manual:Lua_Functions#getStopWatchTime|getStopWatchTime()]], [[Manual:Lua_Functions#getStopWatches|getStopWatches()]], [[Manual:Lua_Functions#getStopWatchBrokenDownTime|getStopWatchBrokenDownTime()]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Using Named Stopwatches === | ||
| + | |||
| + | All variable names can be replaced with a string name. Let's rewrite the above code with named stopwatches instead. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch", true) -- using the name 'Fight Stopwatch' and starting it automatically | ||
| + | |||
| + | -- some time has passed | ||
| + | |||
| + | stopStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch") | ||
| + | echo("The fight lasted for " .. getStopWatchTime("Fight Stopwatch") .. " seconds.") | ||
| + | resetStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Using Persistence === | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is preferable (for [[Manual:Lua_Functions#setStopWatchPersistence|technical reasons]]) to assign a name to a stopwatch that will persist over Mudlet sessions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch") | ||
| + | setStopWatchPersistence("Fight Stopwatch") -- enable this stopwatch to persist over Mudlet sessions | ||
| + | display(getStopWatches()) -- will now show that the stopwatch is persistent | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Manual:Lua_Functions#setStopWatchPersistence|setStopWatchPersistence()]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Not implemented yet! | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Batch Job Timers== | ||
| + | <span style="color:#0000FF">'''Batch Job Timers'''</span> are a form of timer that issue a sequence of commands/scripts according to a certain timeout instead of a single command/script. This is a very important tool if the sequence of commands is important. Timers depend largely on the operating system you are using and it cannot be guaranteed under certain conditions that if you have set up 5 timers to fire after 1.3 seconds that the sequence in which they fire is the same sequence in which they were created. If the sequence of commands is important, you should always use batch job timers as this form of timers guarantees that the sequence of commands is observed. For example: If you want to make an auto-miner bot that digs its way into a gold mine digging left, down, down, right, left, down until a trigger catches a message that indicates that the mine is going to collapse and bury your poor soul unless you run for your life and head out of the mine. In this scenario the sequence of commands is vital as you’d lose your way and die. This is a classical case for a batch job timer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | --> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:59, 13 May 2024
Timer Engine
Mudlet supports four different sorts of timers:
The first can be configured by clicking and will start some code in regular intervals. The others can be used in other scripts you code. All of them are described in more detail below.
Regular GUI Timers
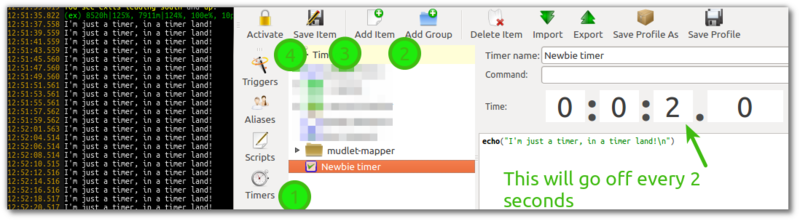
Regular GUI Timers that fire repeatedly in a certain interval specified by the user. To make one, go to the Timers section (1) in Mudlet, click Add (2), select the time periods you'd like the timer to be going off at - save (3) and activate it (4). The timer will go off after your specified interval and then at regular specified intervals after that, until disabled.
You can also enable/disable this timer via scripting with enableTimer() and disableTimer():
enableTimer("Newbie timer") -- enables the timer, so 2s after being enabled, it'll tick - and every 2s after that
disableTimer("Newbie timer") -- disables it, so it won't go off anymoreTemporary Timers
Temporary Timers are timers that go off only once and are the most common type of timer used for scripting purposes. You don't work with them from the Timers section - you just code with them only.
For a basic introduction to temporary timers, read up about them here. Here, we'll continue expanding on what you've learnt so far.
One thing to keep in mind when working with tempTimers is that they are unlike #wait statements you might see in other clients. While #waits are typically cumulative, tempTimers aren't - they go off from the same point in time. Thus if you'd like two timers to go off - one after 3s, and another 1s after the first one - you'd set the second timer to go off at 4s. For example:
tempTimer(3, [[ echo("this is timer #1 going off 3s after being made\n") ]])
tempTimer(4, [[ echo("this is timer #2 going off 4s after being made - and 1s after the first one\n") ]])![]() Note: Temporary timers cannot be accessed from the GUI and are not saved in profiles.
Note: Temporary timers cannot be accessed from the GUI and are not saved in profiles.
Stopping
To stop a temporary timer once you've made it and before before it went off - you use killTimer(). You give killTimer(id) the ID of the timer that you've made - which you get from Mudlet when you make it. Here's an example:
-- get and store the timer ID in the global "greeting_timer_id" variable
greeting_timer_id = tempTimer(2, [[ echo("hello!\n") ]])
-- delete the timer - thus nothing will actually happen!
killTimer(greeting_timer_id)Refreshing
You can also use killTimer() to "refresh" a timer - the following code example will delete the previous timer if one exists and create the new one, thus making sure you don't get multiple copies of it:
if portal_timer then killTimer(portal_timer) end
portal_timer = tempTimer(2, [[ send("enter portal") ]])Time remaining
You can use remainingTime() to check how much time remains on a provided Timer.
tid = tempTimer(600, [[echo("\nYour ten minutes are up.\n")]])
echo("\nYou have " .. remainingTime(tid) .. " seconds left, use it wisely... \n")
-- Will produce something like:
You have 599.923 seconds left, use it wisely...
-- Then ten minutes time later:
Your ten minutes are up.Using variables
To embed a value of a variable in tempTimer code, you might try using this given what you've learnt:
tempTimer(1.4, [[ echo("hello, "..matches[2].."!\n") ]])But that won't work as you'd expect it to - that will try and use the value of matches[2] when the timer goes off - while by then, the variable could have changed! Instead, you take it outside the square [[ ]] brackets - this is correct:
tempTimer(1.4, [[ echo("hello, ]]..matches[2]..[[!\n") ]])
-- or with less brackets:
tempTimer(1.4, function() echo("hello, "..matches[2].."!\n") end)Nesting
If you'd like, you can also nest tempTimers one inside another - though the first [[]]'s will become [=[ ]=]:
tempTimer(1, [=[
echo("this is timer #1 reporting, 1s after being made!\n")
tempTimer(1, [[
echo("this is timer #2 reporting, 1s after the first one and 2s after the start\n")
]])
]=])If you'd like to nest more of them, you'd increase the amount of ='s on the outside:
tempTimer(1, [==[
echo("this is timer #1 reporting, 1s after being made!\n")
tempTimer(1, [=[
echo("this is timer #2 reporting, 1s after the first one and 2s after the start\n")
tempTimer(1, [[
echo("this is timer #2 reporting, 1s after the second one, 2s after the first one, 3s after the start\n")
]])
]=])
]==])Closures
Last but not least, you can also use closures with tempTimer - using a slightly different syntax that has advantages. For example, you have access variables in its scope, when it goes off:
local name = matches[2]
tempTimer(2.4, function() echo("hello, "..name.."!\n") end)Also syntax highlighting will work as expected, because the function will not be given as a string.
![]() Note: In this case, you mustn't use matches[2] directly in the echo() command. It will not work as expected. Instead, bind the it to a new variable like name as seen in the example above.
Note: In this case, you mustn't use matches[2] directly in the echo() command. It will not work as expected. Instead, bind the it to a new variable like name as seen in the example above.
Offset Timers
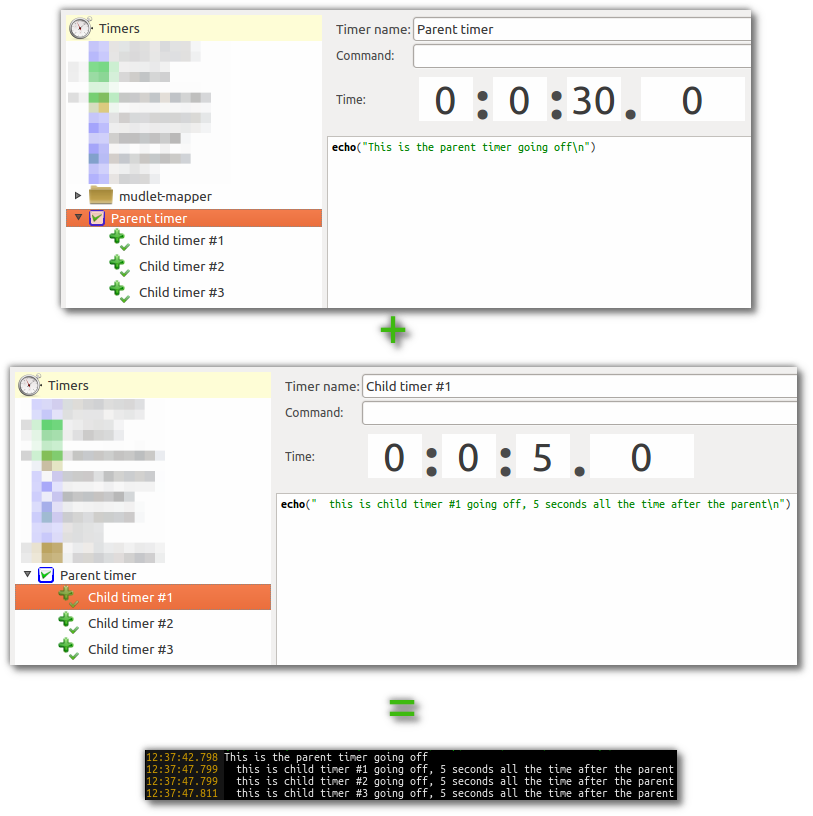
Offset Timers are child timers of a parent timer and fire a single shot after a specified timeout after their parent fired its respective timeout. This interval is an offset to the interval of its parent timer. To make them, add a regular GUI timer (see above), then create another timer and drag it onto the timer. This will make the timer that is "inside" the timer (the child inside the parent) go off at a certain time after its parent goes off. Offset timers differ visually from regular timers and are represented with a + icon for offset. Offset timers can be turned on and off by the user just like any other timer. For example - a parent timer fires every 30 seconds and by doing so kicks off 3 offset timers with an offset of 5 seconds each. Consequently, the 3 children fire 5 seconds after each time the parent timer fired. To make this happen, make the parent timer tic every 30 seconds, drag 3 timers into it with an offset of 5s on each:
Uses and examples
Enable/disable triggers
This'll make use of tempTimer to enable a trigger and disable it after a short period of time:
enableTrigger("Get enemy list")
tempTimer(3, [[disableTrigger("Get enemy list")]])Running a script after the current triggers
A useful trick to get your code to run right after all of the current triggers (GUI and temporary) ran would be to use a time of 0:
-- in a script, this will run after all scripts were loaded - including the system, wherever in the order it is.
tempTimer(0, function()
print("this timer is running after all triggers have run")
end)Have more examples you'd like to see? Please add or request them!
Stopwatches
The stopwatch feature can be used to time how long things take, e.g. long running functions or how long a fight lasts. Stopwatches can be started, stopped and reset just like a regular physical stopwatch. They can also be given a name and made to be persistent, meaning that they can keep running (or timing) when Mudlet has been closed. This gives you the ability to time real-life events. Of course, you can also query how much time has passed and delete a stopwatch no longer required.
Creating and Starting
fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch() -- create, or re-use a stopwatch, and store the watch variable ID in a global variable to access it from anywhere
-- then you start the stopwatch in some trigger/alias/script with;
startStopWatch(fightStopWatch)The watch will now be running. Alternatively, you can create and instantly start a stopwatch in one line;
fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch(true)See also: createStopWatch(), startStopWatch()
Stopping and Resetting
You can stop a stopwatch and retrieve its run time as follows;
-- in a trigger script for example you can write:
fightTime = stopStopWatch(fightStopWatch)
echo("The fight lasted for " .. fightTime .. " seconds.")Then reset it for the next fight.
resetStopWatch(fightStopWatch)Note that resetting a stopwatch does not stop or start it, it's simply resets the time value to zero.
See also: stopStopWatch(), resetStopWatch()
Deleting a Stopwatch
To delete a stopwatch and free up the variable ID simply;
deleteStopWatch(fightTime)See also: deleteStopWatch()
More Ways to Retrieve Running Time
The time can be retrieved at any point of a started and currently running or stopped stopwatch.
getStopWatchTime- returns the time as a decimal number of seconds with up to three decimal places to give a milli-secondsgetStopWatches- returns a table of the details for each stopwatch in existencegetStopWatchBrokenDownTime- returns a table of times for a given stopwatch; days, hours, minutes, etc...
See also: getStopWatchTime(), getStopWatches(), getStopWatchBrokenDownTime()
Using Named Stopwatches
All variable names can be replaced with a string name. Let's rewrite the above code with named stopwatches instead.
fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch", true) -- using the name 'Fight Stopwatch' and starting it automatically
-- some time has passed
stopStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch")
echo("The fight lasted for " .. getStopWatchTime("Fight Stopwatch") .. " seconds.")
resetStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch")Using Persistence
It is preferable (for technical reasons) to assign a name to a stopwatch that will persist over Mudlet sessions.
fightStopWatch = fightStopWatch or createStopWatch("Fight Stopwatch")
setStopWatchPersistence("Fight Stopwatch") -- enable this stopwatch to persist over Mudlet sessions
display(getStopWatches()) -- will now show that the stopwatch is persistentSee also: setStopWatchPersistence()